dB (Decibel)
A decibel (dB) is a dimensionless, logarithmic unit used to express the ratio between two values of a physical quantity, commonly power, intensity, or voltage. ...
The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit expressing ratios of power, voltage, or sound pressure, essential in aviation, engineering, and acoustics.
The decibel (dB) is a fundamental logarithmic unit expressing ratios of power, intensity, voltage, and sound pressure. It is crucial in fields such as aviation, telecommunications, audio engineering, and acoustics, allowing professionals to effectively manage and communicate about vast dynamic ranges in technical systems.
The decibel uses a base-10 logarithmic scale to describe ratios:
For power:dB = 10 × log10(P2/P1)
For quantities proportional to power squared (voltage, sound pressure):dB = 20 × log10(V2/V1)
This approach compresses large numerical spans, simplifies calculations (as multiplication becomes addition), and aligns with how humans perceive changes in intensity or loudness.
Decibels always compare two quantities of the same dimension. Without a reference, “10 dB” only means the measured value is 10 times the power (or 3.16 times the voltage) of the reference. A value of 0 dB signals equality, negative values indicate the measured is lower than the reference, and positive values indicate the measured is higher.
To provide absolute meaning, decibel values often include a suffix that specifies the reference:
| Symbol | Reference Value | Physical Quantity | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| dBSPL | 20 μPa | Sound Pressure | Aircraft noise certification |
| dBA | 20 μPa (A-weighted) | Sound Pressure | Environmental/human-perceived noise |
| dBV | 1 V (rms) | Voltage | Audio equipment, avionics |
| dBu | 0.775 V (rms) | Voltage | Broadcasting, professional audio |
| dBm | 1 mW | Power | RF transmission, aircraft radios |
| dBi | Isotropic radiator | Antenna Gain | Aircraft antenna specification |
| dBFS | Digital full scale | Signal level | Digital audio, cockpit recorders |
For example, dBSPL is used for environmental noise measurement in aviation, referenced to 20 μPa (threshold of hearing), while dBm is standard for radio transmitter power.
dBSPL (Sound Pressure Level):
Used for quantifying sound in air, especially aircraft noise monitoring.
dBA (A-weighted):
Adjusts for human hearing sensitivity, standard in noise exposure and abatement.
dBV/dBu:
Used for audio and avionics signal voltage comparisons.
dBm:
Expresses RF power, vital for aircraft radios, radar, and communication links.
dBi:
Specifies antenna gain relative to an ideal isotropic radiator, key for navigation and communication.
dBFS:
Used in digital audio, with 0 dBFS as the maximum, ensuring no signal clipping.
Aircraft noise is measured in dBA or dBSPL for regulatory compliance (ICAO Annex 16, FAA Part 36). Noise monitoring stations use precision microphones and sound level meters to map exposure, inform community relations, and guide noise abatement.
Avionics, communication, and radar systems rely on dB for specifying amplifier gains, filter attenuations, and transmission losses. Decibel arithmetic (adding gains/losses) streamlines system design.
RF systems in aviation use dBi (antenna gain), dBm (power), and dB (path loss) to ensure adequate signal coverage and performance, as specified in ICAO Annex 10.
Power ratio:
100 W vs. 10 W transmitter:dB = 10 × log10(100/10) = 10 dB
Voltage ratio:
2 V vs. 1 V:dB = 20 × log10(2/1) = 6 dB
Sound pressure (2 Pa vs. 20 μPa):SPL = 20 × log10(2 / 20e-6) = 100 dB
Quick Reference:
| Ratio | Power (dB) | Voltage/Pressure (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| 2× | +3 dB | +6 dB |
| 10× | +10 dB | +20 dB |
| 0.5× (half) | –3 dB | –6 dB |
| 0.1× (1/10) | –10 dB | –20 dB |
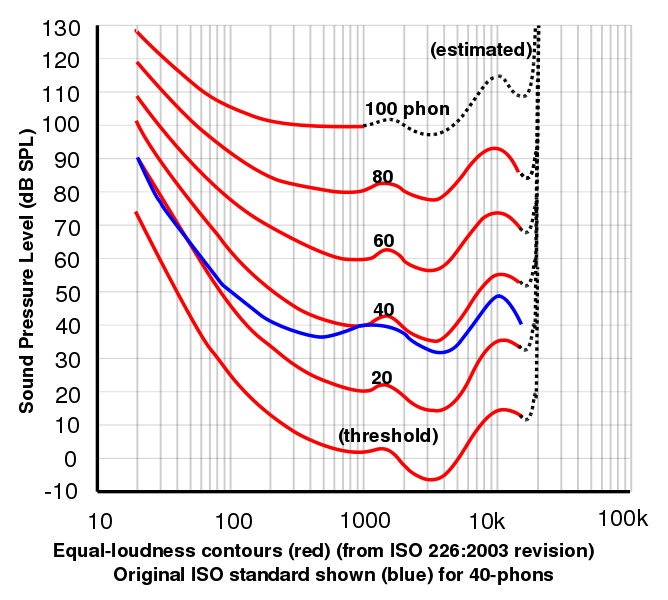
The dB scale matches how humans perceive sound. A 10 dB increase is typically perceived as twice as loud. Frequency weighting (A, C, Z) adjusts measurements for human sensitivity, with dBA being the most common for environmental and occupational noise.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sound Pressure Level (SPL) | Pressure variation from sound waves, referenced to 20 μPa in air (dBSPL). |
| Just Noticeable Difference (JND) | Smallest perceptible change in level, typically around 1 dB for sound. |
| Equal-loudness contour | Curves showing SPL required at each frequency for equal perceived loudness (Fletcher–Munson). |
| A-weighting (dBA) | Frequency weighting to mimic human hearing sensitivity in noise measurement. |
| Effective Radiated Power (ERP) | Transmitter power × antenna gain, in dBm or dBW, key for RF systems. |
| LEQ (Equivalent Continuous Sound Level) | Average SPL over a stated period, used in noise assessment. |
A decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit for expressing ratios of power, voltage, or sound pressure. It is used because it compresses large numeric ranges into manageable figures, simplifies calculations, and aligns with human perception of sound and intensity.
Key references include dBSPL (20 μPa for sound pressure), dBA (A-weighted for human hearing sensitivity), dBV (1 V rms), dBu (0.775 V rms), dBm (1 mW power), dBi (antenna gain vs. isotropic), and dBFS (digital full scale). Each is used in specific technical and regulatory contexts.
A 10 dB increase is generally perceived as a doubling of loudness by the human ear. However, doubling the sound pressure level (a 6 dB increase) is perceived as a moderate increment, not a doubling.
Yes. Negative dB values indicate the measured quantity is below the reference value. For example, -20 dB means the value is 1/100th the power or 1/10th the voltage or pressure of the reference.
Power is proportional to the square of voltage or pressure. The logarithmic identity log10(x²) = 2·log10(x) means power ratios use 10·log10, while voltage/pressure ratios use 20·log10.
Discover how advanced decibel-based monitoring and analysis can ensure compliance with regulatory standards, enhance aviation safety, and improve passenger experience.
A decibel (dB) is a dimensionless, logarithmic unit used to express the ratio between two values of a physical quantity, commonly power, intensity, or voltage. ...
dBm (decibel-milliwatt) is a logarithmic unit used to express absolute power levels, referenced to 1 milliwatt, widely used in RF, telecom, and optical systems ...
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) measures the relative strength of a desired signal compared to background noise, crucial for system performance in electronics, comm...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.