DME (Distance Measuring Equipment)
DME, or Distance Measuring Equipment, is a radio navigation aid in aviation that provides pilots with real-time slant range distance from an aircraft to a groun...
DME is a radio navigation aid that gives aircraft accurate distance measurements to ground stations, supporting safe and efficient navigation across all phases of flight and serving as a key backup to GNSS systems.
Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) is a foundational aviation radio navigation system, providing real-time, accurate slant range distance between an aircraft and a fixed ground station. Operating in the UHF band (960–1215 MHz), DME supports pilots and air traffic controllers with essential distance data for en-route navigation, terminal procedures, and precision approaches. Its role in modern aviation is critical—not just as a stand-alone aid, but as a component of integrated navigation suites (like VOR/DME, ILS/DME, and RNAV systems), and as a terrestrial backup for satellite navigation systems.
DME measures the elapsed time between the transmission of interrogation pulses from the aircraft (interrogator) and the reception of reply pulses from the ground-based transponder. The process is as follows:
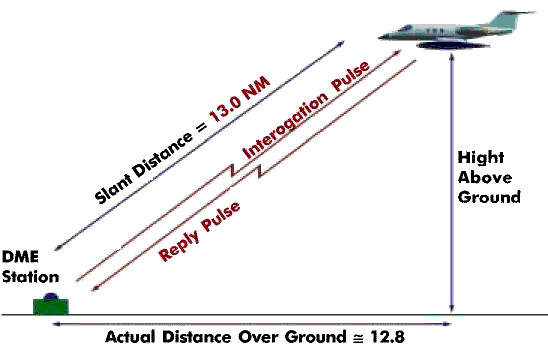
This slant range includes both the horizontal distance and the aircraft’s altitude above the ground station, meaning the number displayed is the straight-line, not ground track, distance.
DME cannot provide bearing or azimuth information; it strictly measures distance. For bearing, it is often paired with VOR or TACAN systems.
DME stations are classified by power and intended use:
| Type | Output Power | Typical Use | Max Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Power DME | ~1,000 W | En-route (w/ VOR) | Up to 199 NM |
| Low-Power DME | ~100 W | Terminal/approach (w/ ILS/LOC) | Local/short |
DME is rarely used alone. Its integration with other aids enables comprehensive navigation:
Modern avionics automate frequency pairing, reducing pilot workload and enhancing safety during busy flight phases.
DME supports all phases of flight:
DME functions within the internationally protected 960–1215 MHz UHF band, using 1 MHz-spaced channels (X and Y modes) for interrogation and reply. Each VOR or ILS frequency is paired (via lookup tables) with a DME channel, simplifying cockpit management and preventing errors.
Pulse pair coding and channel randomization allow multiple aircraft to use the same facility simultaneously without interference. Modern DME ground stations can handle hundreds of interrogations per second.
DME is regulated by ICAO (Annex 10) and national authorities (FAA, EASA). Key requirements include:
Illustration: Slant range (direct line-of-sight) vs. horizontal ground distance. At altitude directly over the station, the DME reading equals the aircraft’s altitude in nautical miles.
Last reviewed: July 23, 2025
This entry is created for tarmacview.com and is intended for pilots, engineers, aviation students, and professionals. Always consult current regulatory and manufacturer documentation before flight or system installation.
DME (Distance Measuring Equipment) is an aviation navigation aid that measures the slant range distance from an aircraft to a ground station by timing the round-trip of radio pulses. The aircraft sends interrogation pulses to a ground transponder, which replies after a fixed delay. The elapsed time—minus the known delay—is converted to distance, displayed in nautical miles. DME only provides distance, not bearing.
DME typically provides slant range accuracy within ±0.2 nautical miles or 3% of the measured distance, whichever is greater. Its update rate and resolution are sufficient for high-speed and precision operations in all phases of flight.
Yes. While GNSS (like GPS) is now primary for navigation, DME is mandated as a backup in many regions and is essential for compliance with certain airspace and procedures, as well as for redundancy in the event of GNSS outages or interference.
Slant range is the straight-line distance between the aircraft and the DME station, incorporating both horizontal and vertical (altitude) components. Directly over a DME at altitude, the distance displayed is the aircraft’s height above the station (in nautical miles).
VOR/DME indicates a navigation facility that provides both azimuth (direction) and distance from a single site, combining VOR and DME. ILS/DME combines precision approach guidance (ILS) with DME distance, often used for step-down fixes and replacing marker beacons on approaches.
Understand DME and other avionics systems to enhance your situational awareness and flight safety. Explore how DME integrates with VOR, ILS, RNAV, and serves as a reliable backup for satellite navigation.
DME, or Distance Measuring Equipment, is a radio navigation aid in aviation that provides pilots with real-time slant range distance from an aircraft to a groun...
Slant range is the direct, line-of-sight distance between two points at different altitudes, crucial in aviation, radar, and remote sensing. It impacts navigati...
An altimeter is an essential aviation instrument for measuring an aircraft's altitude above a reference level, ensuring safe navigation, terrain avoidance, and ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.