Warning Light – Light Indicating Hazardous Condition – Safety Systems
Warning lights are specialized visual safety devices that signal hazardous conditions in industrial and commercial environments, using advanced LED, strobe, or ...
A caution light (yellow warning) alerts drivers to non-critical but important issues in vehicle systems, prompting timely maintenance and safety checks.
Modern vehicles are equipped with complex networks of sensors and electronic control units (ECUs) that monitor the performance and health of critical systems. The dashboard serves as the central interface between these systems and the driver, using illuminated symbols—often color-coded—to provide real-time status updates or alert operators to potential issues. Understanding the meaning of these caution lights is essential for timely response, maintaining safety, and preventing minor issues from turning into major failures.
Dashboard warning lights are color-coded according to international standards (such as ISO 2575 and SAE J2402), applying principles also used in aviation, rail, and industrial machinery:
| Color | Meaning | Typical Action |
|---|---|---|
| Green/Blue | Informational/Confirmation | No action needed; indicates system status |
| Yellow/Amber | Caution/Warning (Non-critical) | Attention required soon; system performance altered |
| Red | Critical Warning/Immediate Action Required | Stop vehicle safely; resolve issue immediately |
Yellow caution lights are specifically designed as advisory indicators, signaling that a system is not functioning optimally but does not pose an immediate hazard. These warnings are based on human factors research: yellow/amber is easily noticed and understood as a warning without causing panic, unlike red, which signals imminent danger.
Below are some of the most common yellow caution lights found in modern vehicles, their significance, and recommended actions.
Definition:
The ABS warning light is a yellow symbol—often labeled “ABS” in a circle or parentheses. It alerts the driver to a malfunction or deactivation of the anti-lock braking system, which is crucial for preventing wheel lockup during emergency braking or on slippery roads.
Indicator Behavior:
Implications:
If the ABS light is on, the standard brakes still work but lack anti-lock assistance, increasing the risk of wheel lockup and loss of steering control during hard braking, especially on slick surfaces.
Recommended Action:
Continue driving with extra caution, avoid sudden braking, and schedule a diagnostic service soon. If accompanied by a red brake warning, stop and seek immediate help.
Definition:
Amber symbols such as a car with wavy lines or labels like “ESP,” “VDC,” or “DSC” represent ESC or TCS warnings. These systems help prevent skidding and maintain control by applying brakes to individual wheels or reducing engine power.
Indicator Behavior:
Implications:
When this light is on, the vehicle’s ability to maintain traction, especially in slippery conditions, is reduced.
Recommended Action:
Drive carefully, especially in adverse weather, and have the system checked soon. If turned off intentionally, re-enable it for normal driving.
Definition:
This yellow symbol, resembling a tire cross-section with an exclamation mark, signals low tire pressure or a TPMS malfunction.
Indicator Behavior:
Implications:
Low tire pressure affects fuel economy, tire wear, and can cause blowouts.
Recommended Action:
Check and adjust tire pressures promptly. If the light flashes, have the system serviced.
Definition:
Usually a yellow triangle with an exclamation mark, this light is an aggregate caution indicator, alerting the driver to check the vehicle’s information display for specific messages.
Implications:
The urgency depends on the accompanying warning or message, which can range from low washer fluid to more significant system faults.
Recommended Action:
Review the dashboard messages and address the indicated issues soon.
Definition:
A steering wheel icon with an exclamation point signals issues in hydraulic or electric power steering systems.
Implications:
Steering may become heavy, especially at low speeds, increasing the risk during emergency maneuvers.
Recommended Action:
Drive cautiously and schedule service. If coupled with other electrical warnings, check the charging system.
Definition:
Indicates non-critical brake issues such as low fluid or worn pads. It is distinct from the red brake warning.
Implications:
Braking performance may be reduced, increasing stopping distances.
Recommended Action:
Check fluid levels, inspect brake pads, and schedule repairs promptly.
Definition:
A yellow icon depicting a seated figure with a circle indicates a fault in the airbag or Supplemental Restraint System.
Implications:
Airbags may not deploy in a collision, increasing injury risk.
Recommended Action:
Do not drive with this light on—schedule immediate repairs, especially if carrying passengers.
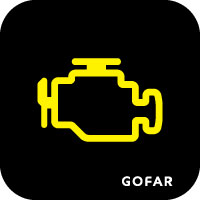
Definition:
A yellow engine-shaped symbol signals engine or emissions-related faults.
Indicator Behavior:
Implications:
Driving with a steady light is usually safe for short periods, but a flashing light requires immediate attention.
Recommended Action:
Check for simple issues (like a loose gas cap), reduce speed if flashing, and schedule diagnostics.
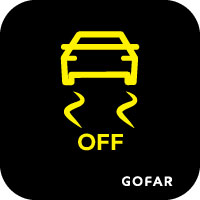
Definition:
A car with squiggly lines and “OFF” means traction control is disabled.
Implications:
Increases risk of wheel spin and loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces.
Recommended Action:
Enable the system if possible. If not, have it serviced.
Definition:
A yellow symbol (car with wrench or “i”) indicates a non-specific system fault.
Implications:
Underlying issues require diagnosis to prevent further problems.
Recommended Action:
Consult dashboard messages and schedule a diagnostic service.
Definition:
A “P” in a circle with an exclamation point signals an issue with the electronic parking brake.
Implications:
Parking brake may not operate properly, increasing risk of vehicle movement when parked.
Recommended Action:
Have the system inspected and repaired.
Caution lights are not unique to vehicles—they are used in aviation, railways, and industrial machinery to denote non-critical but important alerts. For example, aircraft use amber caution lights to highlight degraded performance (e.g., backup hydraulic mode, sensor anomalies) without signaling imminent danger.
Fail-safe Design and Human Factors:
Yellow/amber is reserved for alerts that require the operator’s attention without demanding immediate shutdown. These systems are designed for redundancy and are based on research into human perception and reaction to colors and symbols.
A yellow caution light is an early warning system, designed to catch the operator’s attention before a minor issue becomes a major problem. Understanding what each symbol means and how to respond ensures you maintain both the safety and reliability of your vehicle, and helps avoid costly breakdowns or accidents.
For more information on specific warning lights and advanced safety systems, check your vehicle manufacturer’s documentation or consult a certified technician.
References:
Understanding and respecting caution lights is a key part of vehicle ownership and road safety. If you have further questions, contact your service professional or refer to your owner’s manual.
A yellow caution light means a vehicle system has detected a problem that is not immediately dangerous, but requires attention soon. Examples include low tire pressure, ABS faults, or minor engine issues. Ignoring these warnings can lead to more severe problems.
Generally, you can continue driving with a yellow caution light, but you should address the underlying issue promptly. Refer to your owner’s manual or have a professional check the system to prevent escalation.
Caution (yellow) lights indicate non-critical issues that need attention soon, while red lights signal immediate dangers requiring you to stop and address the problem right away, such as major brake or engine failures.
Most caution light symbols and colors follow international standards (like ISO 2575, SAE J2402), but the exact appearance and behavior may differ by manufacturer. Always consult your owner's manual for specifics.
If several caution lights illuminate simultaneously, check your vehicle’s information display for messages. Address the most urgent issues first and seek professional diagnostics to avoid further damage or safety risks.
Understanding caution lights lets you respond quickly to potential issues and keep your vehicle in top condition. Our experts can help you implement advanced safety systems and provide training for your team or fleet.
Warning lights are specialized visual safety devices that signal hazardous conditions in industrial and commercial environments, using advanced LED, strobe, or ...
A taxiway guidance sign is a standardized, often illuminated airport sign that provides critical navigation, instruction, and safety information for pilots and ...
Taxiway markings are standardized visual cues painted on airport surfaces to guide pilots and vehicles safely and efficiently on taxiways, aprons, and intersect...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.