Candela (cd)
The candela (cd) is the SI base unit of luminous intensity, defining the magnitude of visible light emitted in a given direction as perceived by the human eye. ...
Millicandela (mcd) is a unit of luminous intensity—1/1000 of a candela—used for low-output light sources like aviation indicators and LEDs.
Millicandela (mcd) is a unit of luminous intensity in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one-thousandth (1/1000) of a candela (cd). This fundamental photometric unit is essential for specifying the brightness of low-intensity light sources, such as indicator LEDs, aviation panel lights, and small-scale emitters. The precision offered by the millicandela is indispensable in fields where light levels are critical but relatively low, including aviation, electronics, and safety equipment.
The candela is the SI base unit for luminous intensity, quantifying the amount of visible light emitted by a source in a specified direction. The millicandela is derived simply:
1 millicandela (mcd) = 0.001 candela (cd)
This straightforward relationship enables clear and accurate communication of light levels, especially for small or low-output sources where the candela would be an inappropriately large unit. The SI’s use of decimal submultiples like the millicandela ensures consistency in engineering, scientific, and regulatory contexts worldwide.
The candela is uniquely defined in reference to human visual perception—specifically, by the intensity of monochromatic light at a wavelength of 555 nm (green, where human vision is most sensitive). This definition, refined and reaffirmed by international standards bodies, ensures that all derived units, including the millicandela, are rooted in universal physical constants and human experience.
Photometry is the science of measuring visible light, accounting for the sensitivity of the human eye across different wavelengths. Unlike radiometry, which measures all electromagnetic energy, photometry applies a weighting function mirroring human vision—ensuring that units like the candela and millicandela correspond to perceived brightness.
Luminous intensity quantifies the strength of light in a particular direction, measured in candelas or millicandelas. In aviation, this is crucial for applications such as:
The use of millicandela allows engineers to fine-tune light output for optimal performance and compliance in low-intensity applications.
The candela traces its origins to the brightness of a standard candle, once a practical but inconsistent reference. Modern definitions anchor the candela (and thus the millicandela) to physical constants and human visual response, as established by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) and the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). The current SI definition ensures global consistency—critical for aviation safety and regulatory alignment.
Agencies such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) enforce rigorous photometric standards. Minimum luminous intensities for lighting applications are often specified in millicandelas, with regular testing required for compliance and safety.
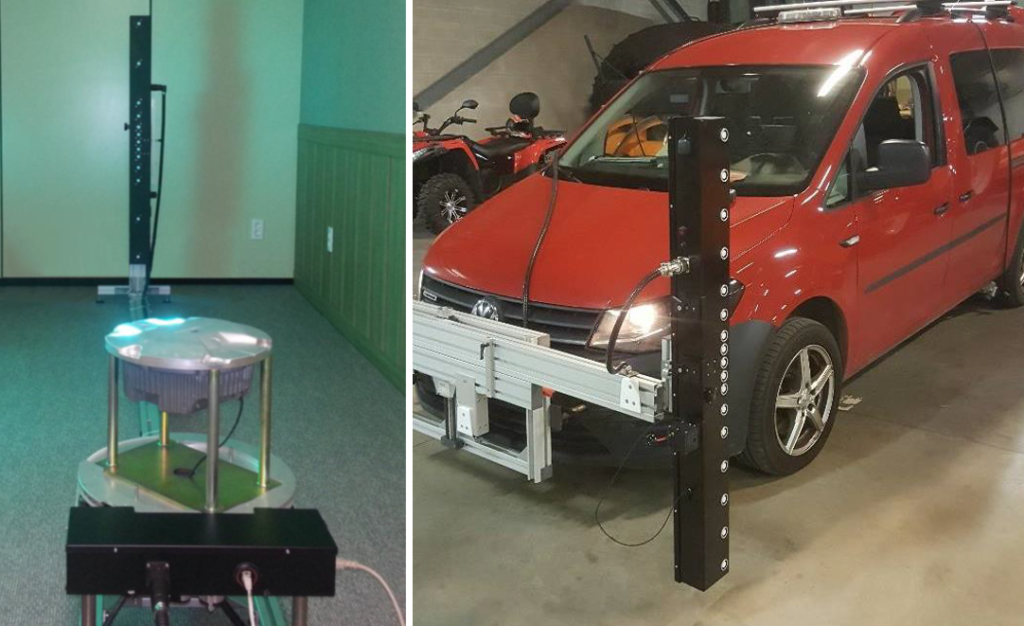
Accurately measuring millicandelas requires specialized photometric equipment:
Laboratory measurement:
Field measurement:
Routine measurement ensures that every light meets regulatory thresholds and maintains operational safety.
Laboratory (left) and mobile (right) photometric measurement setups used for airfield lighting compliance.
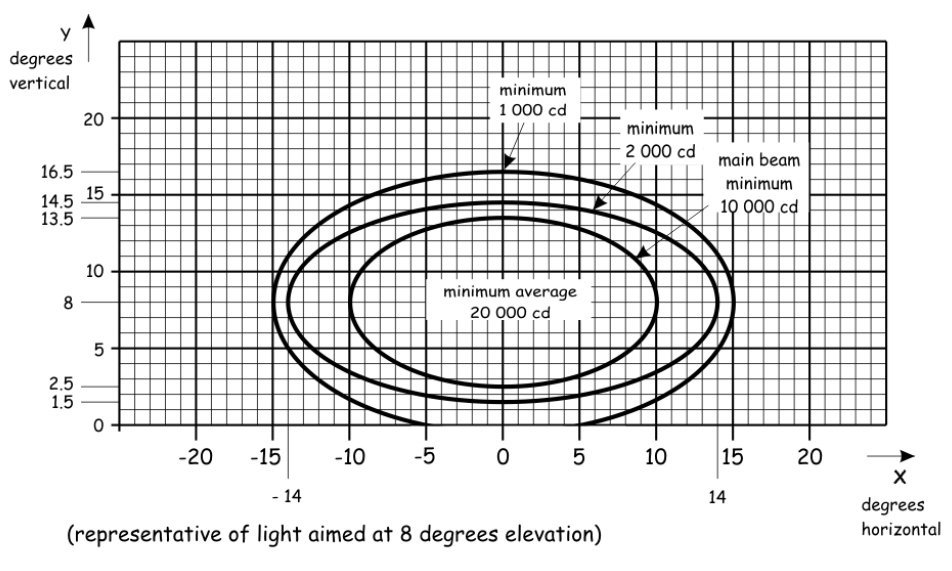
Isocandela diagrams graphically represent a light source’s intensity distribution in space, measured in candelas or millicandelas. They are vital for:
In aviation, isocandela diagrams confirm that approach, runway, and taxiway lights emit within prescribed patterns and intensities.
Isocandela diagram for approach lighting systems, showing intensity distribution in candelas and millicandelas.
| Candelas (cd) | Millicandelas (mcd) |
|---|---|
| 0.001 | 1 |
| 0.01 | 10 |
| 0.1 | 100 |
| 0.5 | 500 |
| 1 | 1,000 |
| 5 | 5,000 |
| 10 | 10,000 |
Example:
A status LED rated at 350 mcd has an intensity of 0.35 cd.
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol | What It Measures | Aviation Example / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd | Light output in a direction per solid angle | Runway edge light, obstruction beacon |
| Luminous Intensity | millicandela | mcd | 1/1000 of a candela | Panel indicators, avionics LEDs |
| Luminous Flux | lumen | lm | Total visible light emitted (all directions) | Interior cabin lighting |
| Illuminance | lux | lx | Light falling on a surface per unit area | Cockpit instrument illumination |
| Luminance | cd/m² | cd/m² | Intensity per area in a given direction | Display screens, sign backlighting |
A steradian (sr) is the SI unit of solid angle. Luminous intensity (cd or mcd) is defined as the luminous flux emitted per steradian, making millicandela ideal for specifying tightly focused directional lights.
An avionics engineer must choose a cockpit LED. Testing finds 20 mcd is too dim in daylight, while 200 mcd is too bright at night. A 100 mcd LED, with dimming capability, provides optimal visibility in all conditions.
ICAO Annex 14 sets minimum and maximum intensities for all airfield lights, often in millicandelas for smaller fixtures.
FAA and EASA require similar standards and regular photometric testing with equipment capable of resolving millicandela intensities.
| Millicandela (mcd) | Candela (cd) | Typical Aviation Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.001 | Very dim panel indicator |
| 10 | 0.01 | Nighttime cockpit indicator |
| 100 | 0.1 | Daylight-visible status LED |
| 500 | 0.5 | Taxiway marker LED |
| 1,000 | 1 | High-intensity beacon or edge light |
Use millicandela values for precision, safety, and global compatibility in specifying and maintaining aviation and electronic lighting systems.
A millicandela is a unit of luminous intensity in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one-thousandth (1/1000) of a candela (cd). It is commonly used to specify low-output light sources like indicator LEDs, control panel lights, and small aviation lighting fixtures.
Both millicandela (mcd) and candela (cd) measure luminous intensity—the strength of light in a specific direction. Lux (lx), on the other hand, measures illuminance, which is the amount of light falling on a surface. Millicandela is used for lower-intensity sources, while candela is for higher-intensity lights.
Millicandela enables precise specification and measurement of the luminous intensity of small, directional aviation lights. This ensures lights are visible at the required distances without being excessively bright, which is vital for safety, regulatory compliance, and efficient operations.
Photometric equipment such as goniophotometers and portable photometers measure luminous intensity. Measurements are typically taken in a dark environment at a standardized distance, with results expressed in millicandelas for low-output sources, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Typical values range from 1–100 mcd for panel indicators and avionics LEDs, 50–500 mcd for taxiway and runway markers, and thousands of mcd for higher-intensity lights. Regulatory bodies specify minimums for each application to ensure adequate visibility.
Ensure your airfield and cockpit lighting meet international photometric standards. Get expert advice on millicandela requirements, testing, and maintenance for optimal safety and regulatory compliance.
The candela (cd) is the SI base unit of luminous intensity, defining the magnitude of visible light emitted in a given direction as perceived by the human eye. ...
Candela per square meter (cd/m²), also known as nit, is the SI unit of luminance. In aviation, it ensures cockpit displays, runway lights, and visual aids are b...
Luminous intensity is a fundamental photometric quantity expressing the amount of visible light emitted by a source in a specific direction per unit solid angle...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.