Lighted Taxiway
A lighted taxiway uses edge lighting to clearly mark taxiway boundaries at airports, improving safety and efficiency for aircraft ground movement at night or in...
Taxiway lights are blue, green, yellow, or red airport lights marking taxiways, intersections, and holding points, guiding safe ground movement in low-visibility or night.
Taxiway lights are a cornerstone of modern airport safety and efficiency, forming a key component of the visual guidance system that enables aircraft and ground vehicles to navigate aerodrome surfaces safely in darkness, fog, rain, or other low-visibility conditions. This glossary entry provides an in-depth look at taxiway lighting: its purpose, types, operational standards, and its critical role in preventing runway incursions and ground incidents.
Taxiway lights are specialized, color-coded lighting fixtures installed along airport taxiways. Their primary role is to delineate taxiway edges, centerlines, intersections, holding points, and transitions, providing visual cues that supplement painted markings and signs. These lights are crucial when visibility is compromised—at night, in fog, rain, snow, or during other adverse conditions.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) standards strictly regulate taxiway lighting systems, specifying the color, intensity, placement, and operation of each fixture. Properly installed and maintained lights minimize the risk of navigation errors, ground collisions, and unauthorized runway crossings (incursions), especially at busy or complex airports.
Modern taxiway lighting systems comprise several specialized light types, each serving a distinct function:
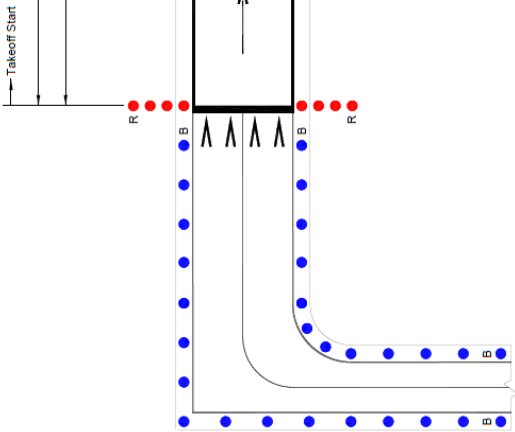
Taxiway edge lights are omnidirectional blue lights marking the boundaries of taxiways and aprons. Typically elevated, they may be recessed in high-traffic or jet-blast areas. Standard spacing is 60 meters (200 feet), but this can be reduced to 30 meters (100 feet) in curves or intersections. At smaller airports, blue reflectors may substitute for powered edge lights.
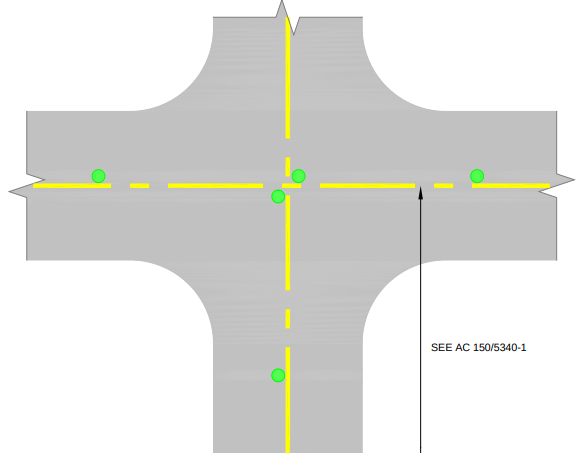
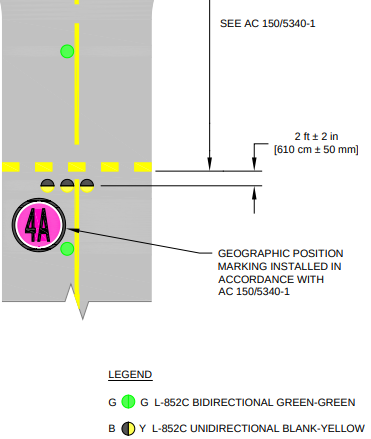
Taxiway centerline lights are in-pavement green lights installed along painted centerlines, providing precise routing—especially important in low-visibility operations or at airports with Category II/III ILS approaches. Standard spacing is 15 meters (50 feet) on straight segments and 7.5 meters (25 feet) in curves or intersections.
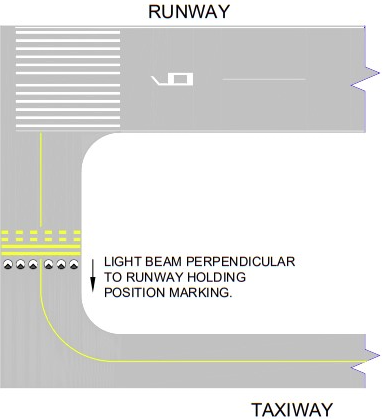
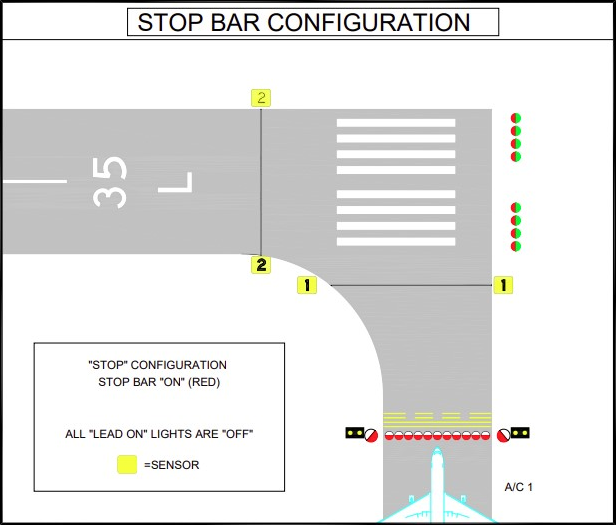
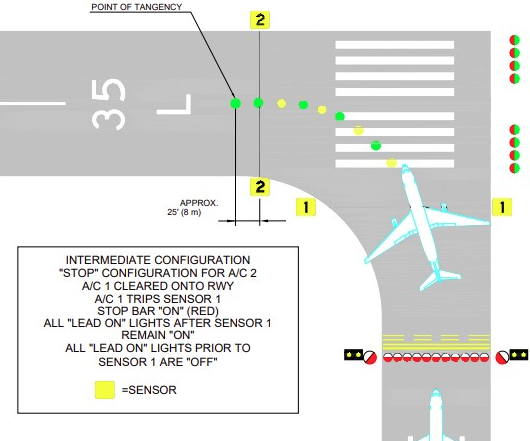
Clearance bar lights consist of three steady-burning yellow (amber) in-pavement lights, installed at designated holding points or intermediate locations. They are especially useful at complex intersections and are vital in low-visibility conditions to ensure pilots and vehicles stop where required.
Runway guard lights (RGLs) are high-visibility yellow lights located at taxiway-runway intersections. They can be elevated “wig-wag” pairs (alternating flashes) or in-pavement arrays. Their purpose is to alert pilots and vehicle operators that they are approaching an active runway and must hold unless cleared.
Stop bar lights are unidirectional red in-pavement lights installed across taxiways just before runway holding points. When illuminated, they indicate an absolute stop—entry to the runway is prohibited. Stop bars are interlocked with ATC and surface movement systems, and only extinguished when it is safe to proceed.
Centerline lead-on and lead-off lights are in-pavement lights marking the transition between taxiways and runways. They display alternating green and yellow, spaced at 7.5 meters (25 feet), and guide aircraft safely onto or off runways, reducing the risk of navigation errors.
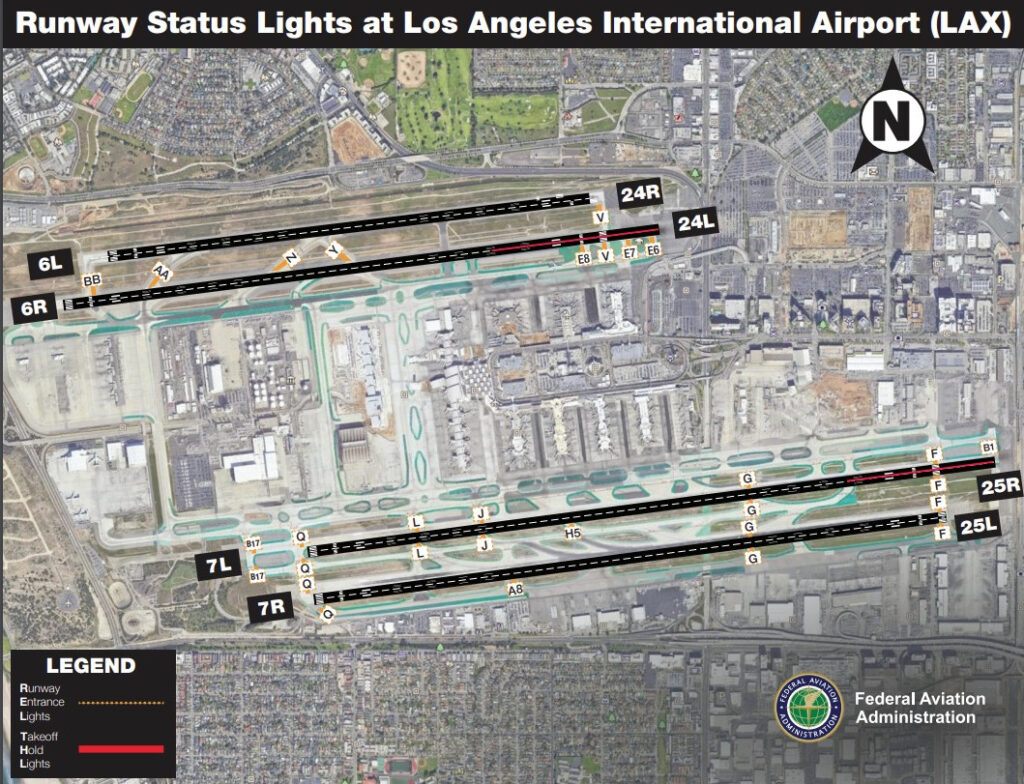
Runway Status Light System (RWSL) is an advanced, automated lighting system using in-pavement red lights—Runway Entrance Lights (RELs) and Takeoff Hold Lights (THLs)—to provide real-time runway occupancy status. RWSL operates independently of ATC using radar and sensors, and pilots are trained not to cross illuminated red RWSL signals, regardless of ATC clearance.
| Color | Meaning/Location | Example Light Type |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | Taxiway edge, apron boundaries | Taxiway Edge Lights |
| Green | Taxiway centerline, safe routing | Taxiway Centerline Lights |
| Yellow | Caution, holding points, transition zones | Clearance Bar, Runway Guard Lights |
| Red | Stop, do not proceed, runway/taxiway incursion barrier | Stop Bar, RWSL |
| Green/Yellow | Transition between runway and taxiway | Lead-On/Lead-Off Lights |
| White | Runway edge/centerline (not taxiway) | Runway Edge/Centerline Lights |
Summary:
This standardized color coding ensures universal comprehension by pilots and ground personnel worldwide, minimizing misinterpretation regardless of location or language.
Taxiway light placement and spacing are defined by ICAO Annex 14 and FAA Advisory Circulars:
Fixtures in jet-blast or high-traffic areas are usually in-pavement; frangible mounts are used for safety.
Taxiway lighting must comply with:
Regular inspection and maintenance are required to:
Modern airports employ LED technology for energy efficiency and reliability.
Taxiway lights are a vital safety system for airport ground operations, enabling precise and safe movement of aircraft and vehicles under all visibility conditions. Their color, placement, and operation are strictly regulated to prevent navigation errors, runway incursions, and ground accidents. As airports grow in complexity and traffic volume, the role of advanced taxiway lighting systems continues to expand, integrating automation and smart technology for enhanced safety and efficiency.
Taxiway lighting uses blue for edges, green for centerlines, yellow for holding points and caution areas, red for stop bars and runway status, and green/yellow for transitions between taxiway and runway. Each color provides specific visual cues to pilots and ground vehicles, ensuring safe navigation, especially under low-visibility conditions.
Taxiway lights provide essential visual guidance for pilots and ground vehicles at night or in poor weather, minimizing the risk of runway incursions, ground collisions, and navigation errors. They work in tandem with surface markings, signage, and radar systems to maintain ground movement safety and operational efficiency.
At major airports, taxiway lights are remotely managed by Air Traffic Control (ATC), often via advanced surface movement guidance and control systems. Automated systems like Runway Status Lights (RWSL) use real-time surveillance data to activate or deactivate lights as needed. Regular maintenance ensures lights meet intensity, color, and reliability standards set by ICAO and FAA.
The main types of taxiway lights are: blue edge lights (marking boundaries), green centerline lights (defining the taxi route), yellow clearance bar and runway guard lights (indicating holding positions and caution zones), red stop bar lights (signaling stop points), and green/yellow lead-on/lead-off lights (guiding transitions between taxiway and runway).
ICAO and FAA regulations require taxiway centerline lights at airports supporting low-visibility operations, such as those with Category II/III ILS approaches. Blue edge lights are standard at airports operating at night or in reduced visibility. Placement and spacing follow international standards for optimal visibility and safety.
Upgrade your airport's taxiway lighting for improved safety, efficiency, and compliance with ICAO and FAA standards. Discover smart lighting solutions for all weather and visibility conditions.
A lighted taxiway uses edge lighting to clearly mark taxiway boundaries at airports, improving safety and efficiency for aircraft ground movement at night or in...
Taxiway centerline lights are green, in-pavement airport lighting fixtures marking the precise taxiway route for aircraft, enhancing safe ground movement in all...
A taxiway guidance sign is a standardized, often illuminated airport sign that provides critical navigation, instruction, and safety information for pilots and ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.