Light Fixture
A light fixture in airport lighting is a complete unit including lamp, optics, housing, and controls, built to rigorous safety and performance standards for air...
A light unit is a single fixture in airport lighting, engineered to guide, mark, or warn as part of the airfield lighting system, crucial for safety.
A light unit in airport lighting is an individual, purpose-engineered fixture designed to provide a specific visual function—guidance, marking, or warning—within an airfield lighting system. Each unit is manufactured to exacting international standards, such as ICAO Annex 14 and FAA Advisory Circulars, which govern optical performance, durability, environmental resistance, and installation. Light units are vital for both airside safety and operational efficiency, giving pilots and ground staff precise visual cues for navigation, even in poor visibility. Their placement and orientation form an integrated, regulated network that enables safe aircraft movement day and night.
Physically, a light unit typically consists of a robust, weather-sealed housing, advanced optics, and a resilient mounting system—either elevated or in-pavement. Modern units predominantly use LED technology for enhanced longevity, energy efficiency, and photometric accuracy. Features like dimmability, remote monitoring, and self-diagnostics are commonplace in contemporary airfield lighting.
Airport operations require a range of specialized light unit types, each optimized for a particular role:
Each type is deployed according to strict standards (e.g., ICAO Annex 14, FAA ACs) for placement, color, intensity, and operational mode.
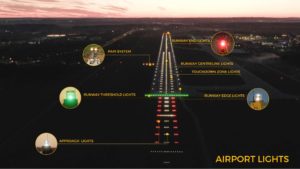
Runway Edge Lights: Placed symmetrically along both runway sides, emitting steady white (transitioning to yellow near the end). Available as elevated (frangible) or in-pavement units.
Threshold Lights: Installed at the runway threshold, emitting green toward the approach direction, often with wing bar extensions for added visibility.
Runway End Lights: Located at the far runway end, emitting red toward departing/overshooting aircraft.
Runway Centerline Lights: Embedded along the centerline, white with red/white and all-red transitions near the end for CAT II/III operations.
Touchdown Zone (TDZ) Lights: White lights in paired rows from the threshold, marking the touchdown area.
REIL (Runway End Identifier Lights): Synchronized flashing white units flanking the threshold for rapid identification.
Runway Guard Lights: Flashing or steady yellow at runway/taxiway intersections to warn of active runways.
All units must withstand environmental extremes, water ingress, and mechanical impacts per regulatory testing.
Taxiway Edge Lights: Steady blue lights along taxiway borders, typically spaced at 60 meters or closer on curves.
Taxiway Centerline Lights: In-pavement green lights marking the taxiway center, especially at complex intersections or runway exits.
Units are engineered for durability against jet blast, chemicals, and vehicle loads, with optics designed to minimize glare.
Approach Lighting Systems (ALS): Extensive arrays of steady and flashing white/red lights extending from the runway threshold, providing alignment and slope cues in low visibility.
PAPI Units: Rows of two or four light boxes, each projecting sharp red/white cutoffs to indicate glide path angle. Correct alignment shows two red and two white lights.
These units have the most stringent photometric and alignment requirements due to their impact on landing safety.
Obstruction Lights: Mark structures that could pose hazards, using steady or flashing red or white lights depending on structure height and criticality. Many units feature automatic intensity adjustment to reduce light pollution.
Airport Rotating Beacon: Emits alternating white/green flashes from an elevated position to indicate the airport’s location at night or in low visibility.
Illuminated Airport Signs: Internally lit signs displaying taxiway/runway designations and directions, using standardized colors and symbols for universal comprehension.
Key regulated attributes of a light unit include:
Each light unit contributes to:
| Scenario | Relevant Light Units | Operational Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Nighttime Operations | Runway edge, threshold, end, centerline, TDZ | High/medium intensity, color coding, programmable intensity |
| Low Visibility (CAT II/III) | Centerline, TDZ, ALS, PAPI | Dense, inset fixtures, redundancy, ALS integration |
| Remote/Temporary Airfields | Solar edge, threshold, REIL, taxiway | Autonomous, portable, quick deployment, SS-SR operation |
| Taxi/Apron Guidance | Taxiway edge/centerline, illuminated signs | Blue/green fixtures, flush mount centerlines, internally lit signs |
| Obstacle Marking | Obstruction lights, barricade lights | Red/white, steady/flashing, scalable |
| Military/Expeditionary Bases | Portable/solar LEDs, PCL, monitoring | Rapid deployment, independent power/control |
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Model | FX862C LED Elevated Runway Edge Light |
| Wattage | 30 W (LED) |
| Voltage | 120-277 V AC |
| Light Output | Steady white (yellow near runway end) |
| Intensity Levels | Programmable: high, medium, low |
| Mounting | Elevated, frangible base |
| Compliance | ICAO Annex 14, FAA L-862, ETL certified |
| Environmental Rating | IP65+, -40°C to +50°C |
| Lamp Life | >50,000 hours (LED) |
| Control Options | Individual, group, or remote (ALCMS, pilot-controlled) |
| Dimming | Step-dimming capability |
Airport light units must comply with:
For further details, refer to:
A light unit is the foundational building block of any airport lighting system. Whether marking a runway edge, guiding a taxiway, or warning of obstacles, each unit’s design, placement, and operation are governed by rigorous international standards to ensure the highest levels of safety and efficiency for airside operations.
For more information or to discuss upgrading your airfield lighting, please contact us or schedule a demo .
A light unit is an individual lighting fixture designed for a specific guidance, marking, or warning function as part of the airport’s airfield lighting system. Each unit is engineered to meet strict performance, durability, and regulatory standards set by ICAO Annex 14 and FAA Advisory Circulars.
Runway light units include edge, threshold, end, centerline, touchdown zone, and runway end identifier lights. Taxiway units include edge and centerline lights, each color-coded and positioned according to strict international standards to guide aircraft safely.
LED light units offer longer life, reduced maintenance, lower energy consumption, precise color and intensity control, and integration with advanced monitoring systems. They outperform traditional halogen or incandescent units in both efficiency and reliability.
Modern airfield light units are managed via Airfield Lighting Control and Monitoring Systems (ALCMS), allowing for remote switching, dimming, diagnostics, and even pilot-controlled operation, enhancing safety and operational flexibility.
Upgrade your airport’s airfield lighting with reliable, energy-efficient light units. Ensure compliance, improve visibility, and maximize operational uptime. Discover our solutions or request a consultation today.
A light fixture in airport lighting is a complete unit including lamp, optics, housing, and controls, built to rigorous safety and performance standards for air...
A luminaire is a complete lighting unit, crucial in airport lighting, integrating optics, electronics, and mounting hardware to deliver precise, safe, and effic...
A fixed light in airport lighting is a non-flashing, continuous illumination used to mark key infrastructure such as runways, taxiways, thresholds, and obstacle...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.