Pavement Marking
Airport pavement markings are critical visual cues painted on runways, taxiways, and aprons, guiding pilots and ground vehicles for safe, efficient airfield mov...
Airport markings are standardized visual patterns painted on runways, taxiways, and aprons, providing critical guidance, boundaries, and safety cues for airport operations.
Airport markings are foundational to the safety and efficiency of airfield operations. These carefully designed and rigorously standardized visual patterns—ranging from lines and stripes to numerals and symbols—are painted on various airport surfaces such as runways, taxiways, aprons, and helipads. Markings provide vital information for pilots, air traffic controllers, ground vehicle operators, and maintenance teams, enabling precise navigation, regulatory compliance, and hazard avoidance on the ground.
Marking (Airport Marking):
A marking is a precisely defined and standardized symbol, line, numeral, or inscription applied to airport surfaces, intended to convey operational information. These markings are engineered for maximum visibility, durability, and clarity, using color-coded paints and often retro-reflective materials to ensure effectiveness under varying lighting and weather conditions.
According to ICAO Annex 14 Volume I:
“A marking is any symbol or group of symbols displayed on the surface of a movement area for the purpose of conveying aeronautical information.”
Markings are not arbitrary; they function as a visual language, instantly recognizable by airport users across the globe. Their consistent application is essential for operational safety, rapid decision-making, and universal understanding in the high-stakes environment of airport ground movement.
Airport markings serve several critical functions:
The standardization of airport markings is paramount for global aviation safety. Regulations and guidance include:
These documents define not just marking appearance, but also inspection and maintenance protocols, ensuring markings remain effective throughout their service life.
Markings are categorized by their operational context:
Each type is specified in regulatory documents for color, width, placement, and meaning.
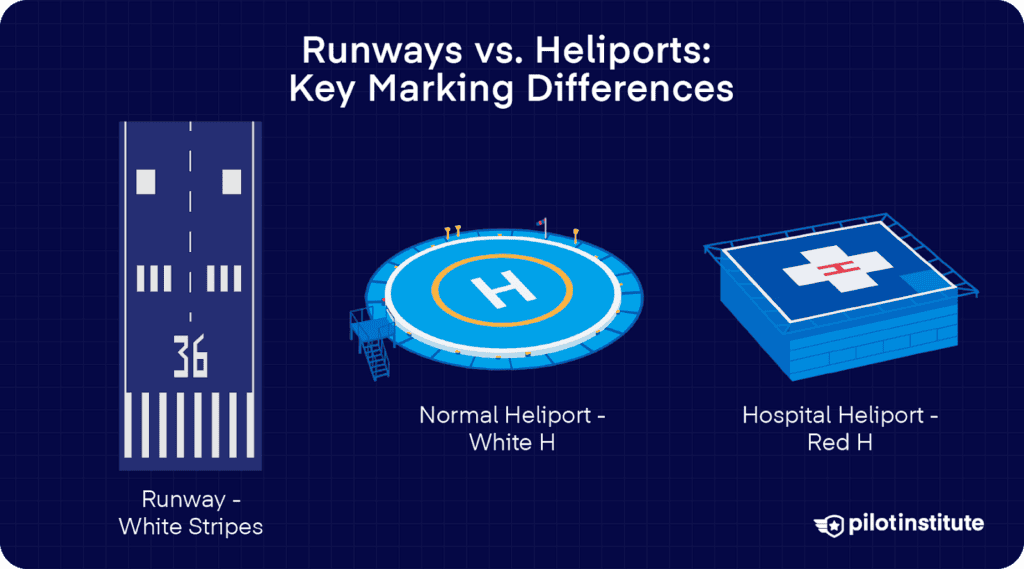
Runway markings are the most prominent and strictly regulated, typically painted in white for maximum contrast and visibility.
Large white numerals indicate the runway’s magnetic heading (rounded to the nearest 10 degrees). Parallel runways add “L”, “C”, or “R” for left, center, or right.
Example: “27L” for Runway 270°, Left.
A dashed white line, aligned with the runway axis, helps pilots maintain direction during takeoff and landing.
Longitudinal white stripes mark the beginning of the usable landing area. The number of stripes increases with runway width.
A solid white bar with arrowheads indicates that the start of the pavement is not suitable for landing but may be used for taxi or takeoff.
Two broad white rectangles, placed symmetrically about the runway centerline 1,000 feet from the threshold, provide a visual aiming reference for landing.
Paired white bars at 500-foot intervals within the first 3,000 feet identify the optimal touchdown area.
Continuous white lines along each runway edge define the usable surface.
Yellow lines or chevrons mark areas not intended for aircraft use.
Large yellow chevrons indicate areas unsuitable for normal operations, often for jet blast or emergency stopping.
Large yellow “X”s signal that a runway is closed for use.
Runway markings, including threshold, centerline, aiming point, touchdown zone, side stripes, and shoulder markings.
Taxiway markings are predominantly yellow, designed for high visibility and clarity.
A solid yellow line guides aircraft and vehicles along the taxiway.
Double yellow lines define the taxiway boundary. Solid lines separate taxiways from non-load-bearing surfaces; dashed lines are used where the taxiway abuts another pavement.
Yellow chevrons indicate areas adjacent to the taxiway unsuitable for aircraft movement.
Yellow with black inscriptions for direction; black with yellow inscriptions for location.
Two solid and two dashed yellow lines at intersections with runways or restricted areas indicate where aircraft must stop unless cleared by ATC.
Solid yellow centerline bordered by dashed yellow lines for 150 feet before a runway holding position, increasing conspicuity.
Taxiway centerline, edge, shoulder, and holding position markings.
Apron markings organize parking, ground vehicle paths, and operational zones.
Lead-in and lead-out lines (solid and dashed yellow) guide aircraft into and out of parking stands or gates.
Define precise parking locations and alignment for different aircraft types.
White or yellow lines and zebra patterns designate authorized ground vehicle routes.
Red or yellow dashed lines, symbols, or painted “NO ENTRY” text indicate restricted or hazardous areas.
To remain effective, airport markings must be maintained for visibility and reflectivity. This includes:
Consistent, clear markings are non-negotiable in modern aviation. They:
Airport markings are far more than paint on pavement—they are a globally standardized language critical for the safe, efficient, and predictable operation of airports. Adhering to ICAO and FAA standards, these markings guide, warn, and inform, helping all airport users share a common operational understanding and minimizing the risk of ground incidents.
For airports, airlines, and operators, investing in high-quality, well-maintained markings is essential for safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Airport runway with clear, standardized markings for maximum safety and operational efficiency.
Airport markings are standardized visual patterns—lines, symbols, letters, or numbers—painted on runways, taxiways, aprons, and other operational surfaces. They provide essential guidance, boundaries, and safety warnings, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft and vehicles. These markings are governed by international and national aviation standards.
International standards are set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in Annex 14, while national standards, such as those in the United States, are provided by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) through Advisory Circulars like AC 150/5340-1M. These standards ensure consistency, safety, and interoperability at airports worldwide.
Markings are crucial for aviation safety. They provide clear visual cues for pilots and ground crews, helping to prevent runway incursions, guide aircraft during takeoff and landing, define operational boundaries, and indicate warnings or restrictions. Uniform markings reduce confusion and miscommunication, especially at large or complex airports.
The three principal categories are runway markings, taxiway markings, and apron/other surface markings. Each serves a unique role: runway markings guide aircraft during takeoff and landing; taxiway markings direct movement between runways and terminals; apron markings organize parking and ground vehicle routes.
Markings use highly durable, color-coded paints, often embedded with reflective glass beads to ensure visibility in low light or adverse weather. Regular inspections and maintenance are required by aviation authorities to uphold clarity, reflectivity, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Discover how modern airport markings and compliance with global standards can improve operational safety and efficiency. Contact us for expert guidance or schedule a demo to see advanced marking solutions in action.
Airport pavement markings are critical visual cues painted on runways, taxiways, and aprons, guiding pilots and ground vehicles for safe, efficient airfield mov...
Airport ground markings guide pilots and ground crews using standardized, painted visual cues on runways, taxiways, and aprons. These markings ensure safe, effi...
Taxiway markings are standardized visual cues painted on airport surfaces to guide pilots and vehicles safely and efficiently on taxiways, aprons, and intersect...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.